A Human Resources Information System (HRIS) modernizes HR management by centralizing data, automating tasks, and empowering HR professionals and employees with self-service portals. It helps HR departments convert manual processes to strategic business functions.
Leaders recognize employee experience as the most important duty of HR, but 36% employees are not satisfied with their current employer, according to a McKinsey Survey. 75% of companies conduct operational workplace planning but don't use strategic software tools.
HR teams can become strategic partners, contributing to business outcomes by proactively shaping workforce strategies using the right tools. HRIS systems offer the structure and scalability that HR teams need to support growth and compliance.
Businesses collect a vast amount of employee data across payroll, performance, and learning modules. The HRIS systems uncover hidden insights from this data through automation, real-time upgrades, and seamless integrations. Beyond streamlining operations, a well-implemented HRIS improves employee experience. Let's explore the key HRIS functions, benefits, and best practices for implementing an HRIS system.
What Is an HRIS and How Does It Work?
A Human Resources Information System (HRIS) is an electronic system that captures, processes, and maintains employee-related information within the HR function. It is the system of record for information from employee files and payroll to performance and compliance data.
Though used interchangeably, HRIS, HCM (Human Capital Management), and HRMS (Human Resource Management System) have different meanings. HRIS most commonly deals with core admin functions such as tracking personnel, payroll, and benefits. HCM encompasses more functions, such as talent and workforce planning.
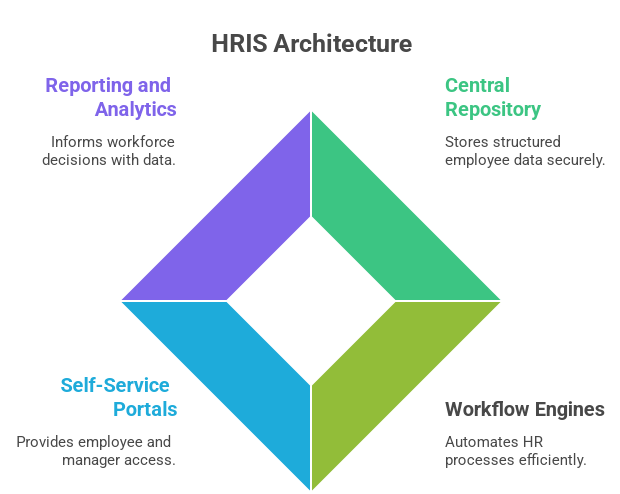
Contemporary HRIS systems can be hosted on-premise or in the cloud, adding flexibility and scale. The main elements of HRIS systems are:
A central repository that stores structured employee information.
Workflow engines for automating HR processes like approvals and notifications.
Employee and manager self-service portals.
Reporting and analytics modules to inform workforce decisions.
An HRIS analyst is responsible for ensuring the integrity of the system. They set up workflows, validate data, facilitate integrations, and provide insights to HR leadership.
These functionalities make it easy for organizations to handle their people management processes. The outcomes are accelerated HR delivery, reduced administrative errors, and enhanced visibility throughout the employee lifecycle. These are critical to agile and compliant HR operations.
Benefits of HRIS: Why Your Company Needs One?
An HRIS is crucial for streamlining efficiency, enhancing compliance, and supporting improved workforce decisions without increasing complexity. Here's what an effectively implemented HRIS brings to your organization:
Automated HR Operations: Manages standard activities such as payroll, leave application, and benefits enrollment, minimizing errors and saving time.
Centralized Employee Data: Keeps all the employee records in a single repository, maintaining accuracy, consistency, and quicker access for auditing or reporting.
Regulatory Compliance: Maintains HR policies consistent with changing labor legislation and automates risk reduction through compliance tracking.
Real-Time HR Analytics: Provides dashboards and reports to track workforce metrics, facilitate planning, and enhance decision-making.
Enhanced Employee Experience: Equips employees with self-service capabilities for pay slips, leave, and notifications, minimizing delays and enhancing satisfaction.
Cost and Time Efficiency: Reduces administrative overheads and rationalizes workflows between locations or departments.
Scalability and Standardization: Expands with your business requirements while ensuring uniform HR processes throughout the company.
Core HRIS Functions Every HR Team Should Know
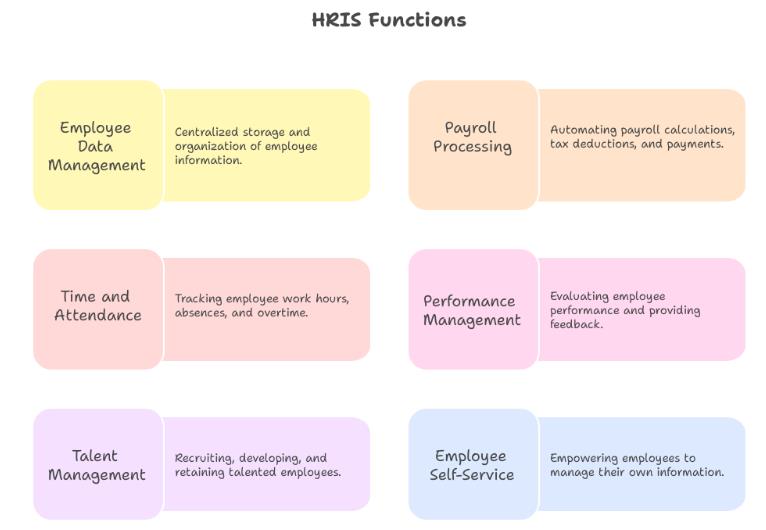
HR teams today face increasing pressure to manage the entire employee lifecycle with precision and speed. A well-designed HRIS simplifies this complexity by centralizing key processes into one system. Below are the core HRIS functions that support scalable, efficient, and compliant HR operations:
Employee Data Management
Organizations handle thousands of data points throughout the employee lifecycle. An HRIS consolidates everything, including contact information, job title, bank accounts, emergency contacts, education records, and more. Clean and accurate data facilitates improved decision-making and minimizes legal risk. It provides one source of truth for all employee records.
Why it matters:
Reduces errors due to manual inputs
Enhances audit compliance and legal reporting
Supports correct insights for workforce planning
Tips:
Impose standardized input fields at every data entry point
Perform regular data validation checks quarterly to eliminate duplicates or stale information
Grant role-based access permissions to safeguard sensitive information
Payroll Processing and Benefits Administration
An HRIS eliminates payroll mistakes through automated processes for gross-to-net calculations, deductions, tax codes, and direct deposits. It also administers employee benefits such as insurance, reimbursements, and retirement contributions. Integration with statutory applications provides error-free compliance.
Why it matters:
Avoids delays and disputes in payroll
Reduces administrative workload on HR and finance staff
Creates employee trust by making accurate, timely payments
Tips:
Integrate payroll modules with attendance and tax applications
Process test payroll cycles before go-live to flag logic gaps
Give a clear pay slip breakdown in the employee portal
Time and Attendance Management
An HRIS enables employers to monitor attendance via biometric technology, mobile devices, or swipe cards. It streamlines overtime, leave, and late entry calculations, providing real-time visibility into the workforce and policy compliance.
Why it matters:
Stops time theft and buddy punching
Facilitates compliance with labor regulations and shift laws
Assists in managing workforce capacity and productivity
Tips:
Utilize geolocation tagging for off-site check-in
Create automated rule-violation alerts (e.g., skipped punches)
Sync attendance information directly with payroll for smooth processing
Performance Management
Automated goal setting, appraisal processes, manager comments, and 360-degree feedback are enabled in HRIS systems. This simplifies the review process, prevents bias, and maintains alignment of employee performance and business strategy.
Why it matters:
Enhances accountability and motivation within teams
Delivers quantifiable KPIs for talent growth
Supports data-driven promotion and succession planning
Tips:
Establish quarterly or half-yearly review cycles in the system
Connect goals to team KPIs for improved alignment
Utilize historical appraisal data to inform future upskilling or promotions.
Talent Management
From job listings to onboarding and career management, an HRIS keeps talent pipeline moving effortlessly across the organization. Applicant tracking, interview scheduling, onboarding processes, and training modules may all be centralized.
Why it matters:
Reduces time spent on hiring and manual effort
Enhances the first-week experience of new joiners
Encourages internal talent mobility and retention
Tips:
Implement automated workflows for onboarding checklists and paperwork
Monitor hiring funnel statistics to identify inefficiencies
Establish internal job boards to foster lateral movement
Employee Self-Service
Self-service portals allow employees to self-update personal information, download payslips, request leave, and verify benefits without creating HR tickets. It increases transparency and eliminates back-and-forth.
Why it matters:
Relieves HR from admin requests
Enhances employee satisfaction with real-time access
Eliminates errors from second-hand updates
Tips:
Offer portal training to workers frequently
Monitor frequent questions to enhance the UI or the knowledge base
Establish alerts for any significant data changes (i.e., bank information)
How to Choose the Right HRIS Solution
Selecting the proper HRIS solution is not an IT choice. It's a strategic initiative that sets the course of HR functionality for years to come. The appropriate platform must match your company goals, HR sophistication, workforce size, and compliance requirements. The wrong choice will lead to data silos, suboptimal adoption, and process failures. Some of the essential assessment criteria for HR organizations making this important decision are:
Know Your HR Requirements and Objectives
Before vendor hunting, determine what you need the HRIS to address.
Compliance or data fragmentation issues?
Need to ramp up hiring or enhance performance monitoring?
Integration with current systems critical?
Tip: Take an internal HR audit and rank requirements across functions such as payroll, benefits, performance, and employee self-service.
Assess Core and Advanced Features
Basic HRIS solutions address payroll, data handling, and leave tracking. Current systems provide strategic HR capabilities such as:
Talent acquisition
Workforce analytics
Compensation planning
HCM suite capabilities
Tip: Develop a feature checklist for must-haves vs. good-to-haves. Select a solution that scales with your needs.
Evaluate User Experience and Adoption Potential
A system isn't beneficial if no one uses it. Find a platform that can be easily adopted by both technical and non-technical employees.
Search for easy navigation and mobile responsiveness
Give preference to platforms with simple employee self-service portals
Tip: Ask for demo access and engage real users, HR teams, managers, and employees in the review.
Verify Compatibility with Current Systems
HRIS is useful only when it can co-exist with your current systems. Verify Easy Integration with:
Payroll software
Accounting software
ERP or ATS systems
Tip: Inquire about APIs available and case studies of integration with systems your team currently uses.
Vendor Support and Roadmap to Consider
An effective HRIS vendor would provide:
Dedicated onboarding assistance
Regular updates and roadmap visibility
Local compliance conformity
Tip: Check SLAs, customer success feedback, and post-sales support assurances.
HRIS Implementation: What to Expect
Deploying an HRIS requires careful planning, cross-functional cooperation, and rigorous attention to detail. Though the result may hugely enhance HR productivity, the process necessitates a structured approach to prevent expensive missteps. Employ role-based access, audit trails, and encryption policies to ensure data security. Implement periodic data reviews to avoid compliance threats.
The process typically takes five phases:
Planning: Establish objectives, success factors, and timelines. Align with general HR and IT strategies.
Configuration: Tailor the system to represent organizational structure, processes, and policies.
Data Migration: Sanitize, validate, and transfer legacy HR data to the new system.
Training: To achieve adoption, provide system knowledge to HR teams, IT, and end users.
Rollout: Roll out in phases or simultaneously, with post-launch support and feedback loops.
Key stakeholders involved in implementing HRIS are:
HR initiates process design and oversees the system to accommodate compliance and workflows.
IT ensures technology integration, security, and infrastructure readiness.
External Vendors provide platform knowledge, configuration advice, and go-live support.
While implementing HRIS, you might encounter these problems:
| Problem | How to Solve it? |
|---|---|
| Inconsistencies in data | Perform a pre-migration audit |
| Resistance from users | Engage users upfront; provide customized training |
| Slippage in timeline | Incorporate buffer time and realistic milestones |
How to Maximize ROI from Your HRIS Investment
A properly implemented HRIS can yield quantifiable returns if it's utilized strategically. The secret is to map the system's features with business objectives, enhance operating efficiency, and create long-term value through the employee lifecycle.
Understand the Cost Drivers
To measure ROI correctly, include all costs involved:
Software licensing per annum or per-user charges based on the HRIS platform.
Implementation, including setup, data migration, and training services.
Support and maintenance, such as vendor SLAs and continuous technical assistance.
Integrations with payroll, time tracking, or applicant tracking systems.
Measure these costs against time saved, errors eliminated, and HR productivity improvements.
Measure Impact Across HR Functions
Leverage HRIS Data for forecasting. Utilize real-time HR information to facilitate workforce analytics. Identify gaps in hiring, training requirements, and patterns of employee attrition. These insights inform improved planning and budgeting decisions.
Darwinbox: A Modern HRIS Built for the Entire Employee Lifecycle
Darwinbox is an all-inclusive human resources information system (HRIS) that assists HR professionals in managing the employee lifecycle with accuracy and ease. It's designed to manage core HR processes, automate workflows, and enhance employees' experience across the board from onboarding to offboarding.
Darwinbox's capacity consolidates complex HR processes into one smart platform. The software solution consolidates talent management, payroll processing, benefits administration, attendance records, and performance management into a single cloud-based HRIS. It also provides mobile-first access, AI-powered insights, and employee self-service portals, enabling HR teams and employees.
Real World Success Stories
ADA (Digital Services Company)
Darwinbox revamped ADA's HR functions, freeing up more than 1,600 employee hours yearly. Time invested in HR activities such as policy approvals, resignation processing, and employee data management went down significantly. QA and helpdesk functions were automated, enhancing HR productivity and streamlining compliance monitoring.
Suzlon (Renewable Energy)
Suzlon saw 50% less manual workloads with Darwinbox. Real-time workforce dashboards replaced cumbersome Excel reports. Attrition and diversity data tracking automatically saved 12–18 hours of report time, allowing leadership to respond quicker to workforce trends.
Bigbasket (E Commerce / Logistics)
Bigbasket processes thousands of travel and expense requests per month. Automating Travel & Expense workflows, Darwinbox provides policy enforcement at a granular level and real-time reporting. This went on to minimize delays and enhance the accuracy of claims in 70+ locations.
Best Practices for Using HRIS Effectively
The level of long-term gains derivable from an HRIS is concerned not simply with implementational schemes, but essentially with how effectively firms use the system in their daily operations, sustain data integrity, and learn to adapt to changing requirements. Some of the best practices that offer consistency in performance, employee uptake, and strategic impact are:
Regular training of HR personnel and end-users
A common cause of HRIS failure is inadequate user training. Where employees do not have a clear picture of the system in their minds, efficiency is compromised, and data quality suffers.
In the case of a training program, all users must be trained with clear knowledge of important features, process updates, and compliance specifications. These short, role-specific sessions should be planned for at least once every three months, immediately following any major system maintenance. Such training provides easy recall and boosts confidence across the organization.
Data hygiene and periodic audits
Effective HR decision-making depends upon timely and relevant data. Without routine audits, errors compound and cast doubt on the veracity of reports and forecasts. Organizations must have monthly checks in place on key data fields such as employment status, pay, and reporting relationships. Automatic validation rules and consistent input formats can also rule out manual errors and further improve the reliability of the system.
Deploying analytics for proactive HR
HRIS systems provide deep insights when they proactively use the data. Rather than make retrospective changes, HR can use forecasts from dashboards that show workforce trends, identify areas of risk, and adjust workforce planning. Some metrics can be viewed from a strategic planning standpoint rather than simply reacting to pain points, such as attrition rate, hiring rate, and time-to-fill.
Keeping HRIS updated with changes in workforce trends
The parameters of HRIS that worked in the conventional setup may be ineffective in a hybrid or competency-driven framework. Organizations should reevaluate the applicability of their HRIS every twenty-four months. Such examination entails an audit of workflows, refinement of policies, and inclusion of new functionalities or integrations aligning with newer priorities, such as internal mobility, DEI, or management of contingent workers.
Full integration between payroll and time tracking
Standalone systems cause friction between attendance, leaves, and payroll processing. A truly integrated HRIS eliminates errors, regulatory issues, and reconciliation challenges. With time and payroll integrations, organizations can reduce discrepancies and improve accuracy. Prior to kick-off, teams should run parallel payroll simulations focusing on calculations and the smooth flow of data.
Maintaining an active feedback loop with users and stakeholders
User feedback is key to pinpointing pain points and driving adoption. Having a feedback mechanism through periodic surveying or user-group meetings helps to iron out issues early on and make improvements to the system. Regularly keeping the conversation going also builds engagement and ensures the HRIS system evolves with the real business needs.
Conclusion
A properly implemented HRIS is no longer a back-office application; it's a strategic asset. It streamlines routine HR processes, enhances data quality, and enables HR groups to engage in business impact as opposed to administrative work. HRIS facilitates forward-looking decisions, whether hiring at scale, planning workforce growth, or monitoring skills development.
Legacy systems hinder HR's capacity to move quickly and remain compliant. Investing in an HRIS that can scale means your organization remains poised for change, whether it's a policy change, a move to remote work, or a requirement to enhance internal mobility.
If your existing HR tools are fragmented and slow, it’s time for a change. With systems like Darwinbox providing mobile-first, AI-driven capabilities, the time to future-proof your HR function has never been better. Select a solution that evolves with you and empowers your workforce at each stage.
FAQs
What are the fundamental HRIS functions?
An HRIS usually manages core HR functions like employee record administration, payroll, attendance, leave tracking, benefits management, and reporting. Additional modules for recruitment, onboarding, performance, and learning are available with some systems.
How does HRIS enhance employee data management?
HRIS consolidates all employee data within a single secure environment, minimizing manual effort and mistakes. It guarantees that information is consistent, available, and updated in real time, thus making reporting and compliance simpler for HR staff.
How is HRIS different from HCM systems?
HRIS is concerned with administrative HR activities such as data, payroll, and compliance. HCM (Human Capital Management) solutions are more comprehensive and encompass strategic components like talent management, succession planning, and employee engagement modules.
Is time and attendance tracking supported in HRIS software?
Yes, time tracking, shift scheduling, and leave administration typically come as integrated modules or add-ons in most current HRIS software. This facilitates precise payroll processing and enhances compliance with labor laws.
In what ways is a cloud-based HRIS advantageous for HR processes?
Cloud-based systems allow real-time access, enhanced security, and simplified updating. They handle remote and hybrid teams seamlessly, lower IT overhead, and provide scalable solutions as business demands expand.